AWS has just announced Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) Managed Instances. This new compute option provides developers with the operational simplicity of a managed service while retaining the flexibility and control of EC2.
With ECS Managed Instances, AWS takes care of infrastructure provisioning, scaling, patching, and cost optimization, while customers enjoy full access to the broad range of Amazon EC2 instance types. This means you get the best of both worlds: the hands-off experience of AWS-managed infrastructure, and the fine-grained performance tuning that comes with EC2.
In this post, we’ll dive into:
- What Amazon ECS Managed Instances is
- The console experience for creating an ECS cluster with Managed Instances
- Key features and benefits
- How it differs from ECS on unmanaged EC2 and ECS Fargate
- When to choose Managed Instances vs other ECS compute options
What is Amazon ECS Managed Instances?
Amazon ECS Managed Instances is a fully managed container compute environment. Instead of manually managing EC2 instances in your ECS cluster, AWS does it for you.
You no longer need to worry about:
- Picking the right EC2 instance sizes and types (unless you want to override defaults)
- Scaling instances up or down
- Applying OS and security patches
- Optimizing task placement for cost efficiency
Instead, AWS automatically provisions, scales, patches, and optimizes your EC2-based cluster.
Behind the scenes, ECS Managed Instances run on Bottlerocket, AWS’s purpose-built container OS. This provides a lightweight, secure, and optimized environment for running containerized applications.
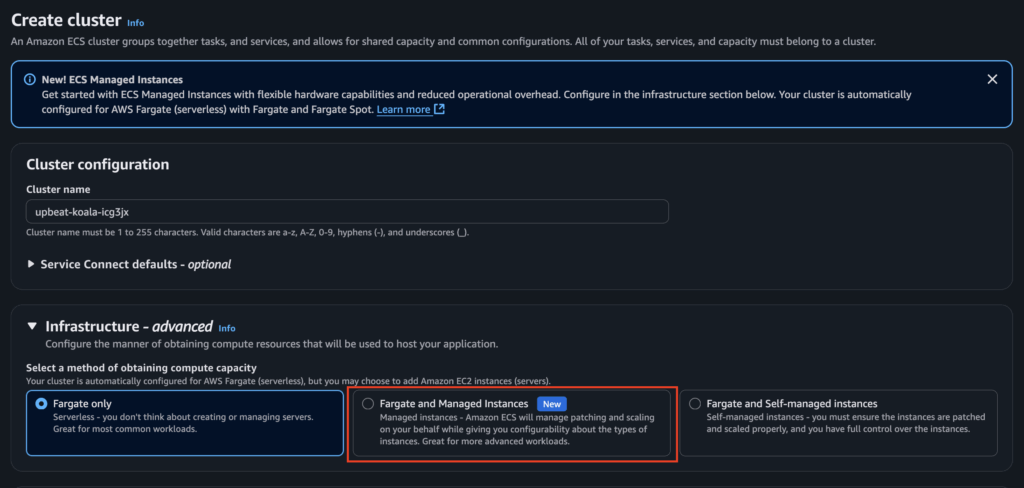
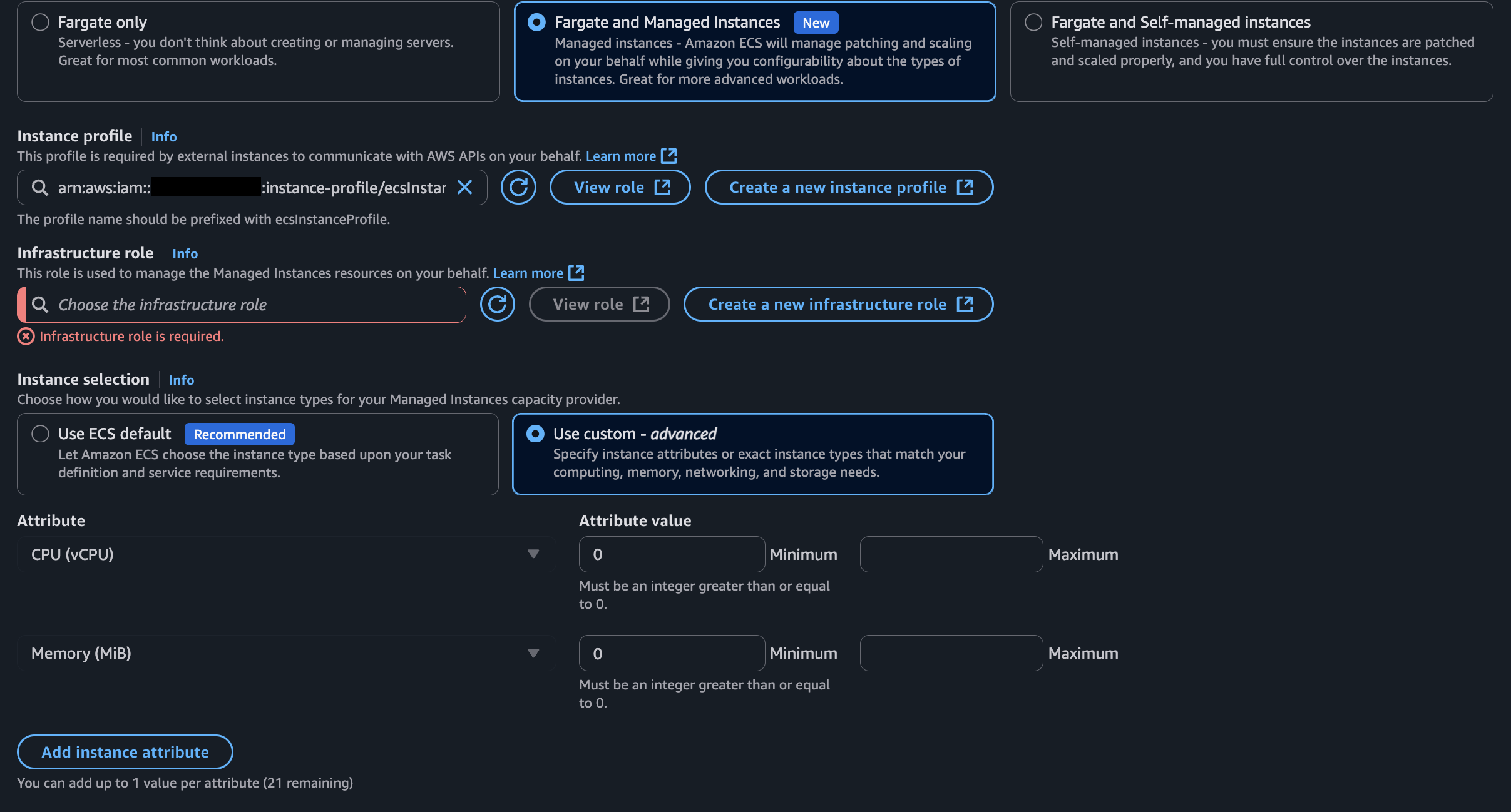
The Console Experience
When you create a new ECS cluster in the AWS Management Console, you’ll now see an option to use ECS Managed Instances alongside Fargate.
You’re presented with two choices:
- Use ECS default – ECS selects the most cost-optimized general-purpose instances for you. AWS evaluates pending tasks and provisions instances that balance cost, performance, and resilience.
- Use custom – advanced – You can define fine-grained attributes for your instances. By default, you see CPU and Memory as filters, but you can choose from 20+ attributes, including:
- GPU support
- CPU architecture (x86, ARM/Graviton)
- Network performance
- Storage requirements
After applying your filters, ECS shows you the matching EC2 instance types and provisions them automatically.
Once configured, your cluster is created and ECS handles ongoing operations, including instance lifecycle management.
Key Features of ECS Managed Instances
Here are the highlights of this new compute option:
1. Fully Managed Infrastructure
- AWS handles provisioning, scaling, and patching of instances.
- Security patches are automatically applied every 14 days.
- You can schedule updates via EC2 event windows to avoid disruption.
2. Flexible Instance Type Selection
- Default mode: ECS auto-picks cost-optimized instances.
- Advanced mode: Specify attributes like GPU acceleration, ARM CPUs, or high-network throughput.
3. Cost Optimization
- ECS consolidates tasks onto fewer instances when possible.
- Idle (empty) instances are automatically drained and terminated.
- Larger instances are leveraged to run multiple tasks efficiently.
4. Seamless AWS Integration
- Supports all EC2 pricing models (On-Demand, Spot, Savings Plans).
- Integrates with IaC tools like AWS CDK and CloudFormation.
5. Security by Design
- Powered by Bottlerocket OS, purpose-built for containers.
- Automated patching and updates maintain a secure runtime.
How ECS Managed Instances Compare to Other ECS Compute Options
Amazon ECS now offers three primary compute options:
| Feature | ECS on Unmanaged EC2 | ECS Fargate | ECS Managed Instances |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | You manage provisioning, scaling, AMIs, and patching | Fully serverless – AWS manages everything | AWS manages instances (provisioning, patching, scaling) |
| Control over Instance Types | Full control over EC2 instance types | No control – AWS fully abstracts compute | Flexible: AWS auto-selects, or you specify attributes |
| Scaling | Manual or auto scaling via ASGs | Automatic scaling (task-based) | Automatic instance scaling and task placement |
| Security Patching | Your responsibility | Fully AWS-managed | AWS-managed (14-day cycle) |
| Operating System | Choice of AMI (Amazon Linux, Bottlerocket, custom) | AWS-managed Fargate runtime | Bottlerocket (managed by AWS) |
| Use Case Fit | For advanced users needing custom AMIs, kernel modules, or deep EC2 tweaks | For serverless container workloads needing zero ops | For users wanting EC2 flexibility without infra headaches |
When to Use ECS Managed Instances
- ✅ Best fit if: You want EC2-level control (specific instance types, GPUs, Graviton processors) but don’t want to manage scaling, patching, or provisioning.
- ✅ Great for ML workloads, high-performance computing, or cost-sensitive apps that need EC2 flexibility.
- ✅ Works well if you want Spot + On-Demand blends for maximum cost savings.
When to Use ECS on Unmanaged EC2
- 🚀 If you need complete control over EC2, including:
- Custom AMIs with special drivers
- Kernel modifications
- Integration with legacy applications requiring VM-like management
- ⚡️ More work, but maximum flexibility.
When to Use ECS Fargate
- 🔥 If you want serverless containers and don’t care about the underlying infrastructure.
- 💡 Perfect for small teams or microservices architectures where agility and simplicity outweigh cost optimizations.
Conclusion
Amazon ECS Managed Instances is a powerful middle ground between ECS on EC2 and ECS Fargate, offering the operational simplicity of Fargate with the flexibility and control of EC2. By offloading infrastructure management tasks such as provisioning, scaling, and patching to AWS, while still allowing customers to choose instance families and attributes, it delivers the ideal balance of performance, security, and cost efficiency for containerized workloads.
It’s available today in North Virginia, Oregon, Ireland, Cape Town, Singapore, and Tokyo regions. You can get started via the AWS Management Console, CLI, CDK, or CloudFormation.