Amazon Web Services (AWS) has just rolled out an exciting update for Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS): ECS Exec is now available directly in the AWS Management Console.
This long-awaited feature allows you to open a secure, interactive shell session with your ECS containers without leaving the console. Previously, ECS Exec was only available through the AWS CLI, SDKs, or APIs—forcing developers and operators to switch tools during critical troubleshooting moments. With this update, you can now securely connect to containers with a single click, streamlining debugging, diagnostics, and operational workflows.
Why This Matters
ECS customers often need to interact with containers for:
- Debugging failing applications
- Checking running processes
- Collecting logs or diagnostic information
- Performing break-glass access in production emergencies
Traditionally, this required SSH access, key management, or inbound ports—all of which add unnecessary complexity and security risks.
ECS Exec solves these problems by leveraging AWS Systems Manager Session Manager behind the scenes. This ensures:
- No need for SSH keys
- No inbound ports to manage
- Fully auditable sessions (via CloudTrail & logs)
- Encryption with AWS KMS support
What’s New in the Console
Now, from the ECS console, you can:
- Enable ECS Exec when creating or updating a service/task.
- Configure encryption and logging at the cluster level.
- Navigate to a task’s details, select a container, and click “Connect” to start an interactive CloudShell session.
- View the underlying AWS CLI command, which you can copy or adapt for your local terminal.
This greatly reduces context switching and speeds up troubleshooting.
Supported Environments
ECS Exec works across:
- Linux containers on Amazon EC2 (all ECS-optimized AMIs, including Bottlerocket)
- Linux & Windows containers on AWS Fargate
- Windows containers on ECS-optimized Windows Server 2019, 2022, and 20H2 AMIs
- External instances via ECS Anywhere
Note: ECS Exec requires SSM Agent support, so ensure your environment is compatible.
Security and Access Controls
- ECS Exec sessions run via IAM-controlled policies, giving fine-grained access to who can execute commands.
- Logs (commands + output) can be stored in CloudWatch Logs or Amazon S3 for auditing.
- Sessions are encrypted using TLS 1.2 by default, with the option to use your own AWS KMS CMK.
- All activity is recorded in AWS CloudTrail.
This makes ECS Exec both secure and auditable, making it suitable for both development and production scenarios.
How to Exec Into an ECS Container
Here’s a quick step-by-step guide based on AWS’s best practices.
Step 1: Enable ECS Exec for Your Task or Service
When creating/updating a service:
aws ecs create-service \
--cluster my-cluster \
--task-definition ecs-exec-task \
--enable-execute-command \
--service-name ecs-exec-service \
--launch-type FARGATE \
--network-configuration "awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=[subnet-12345],securityGroups=[sg-12345],assignPublicIp=ENABLED}" \
--desired-count 1
Confirm that ECS Exec is enabled:
aws ecs describe-tasks \
--cluster my-cluster \
--tasks task-id
You should see "enableExecuteCommand": true in the output.
If you are creating a Task from the UI, the screenshot below shows what needs to be ticked to enable ECS Exec
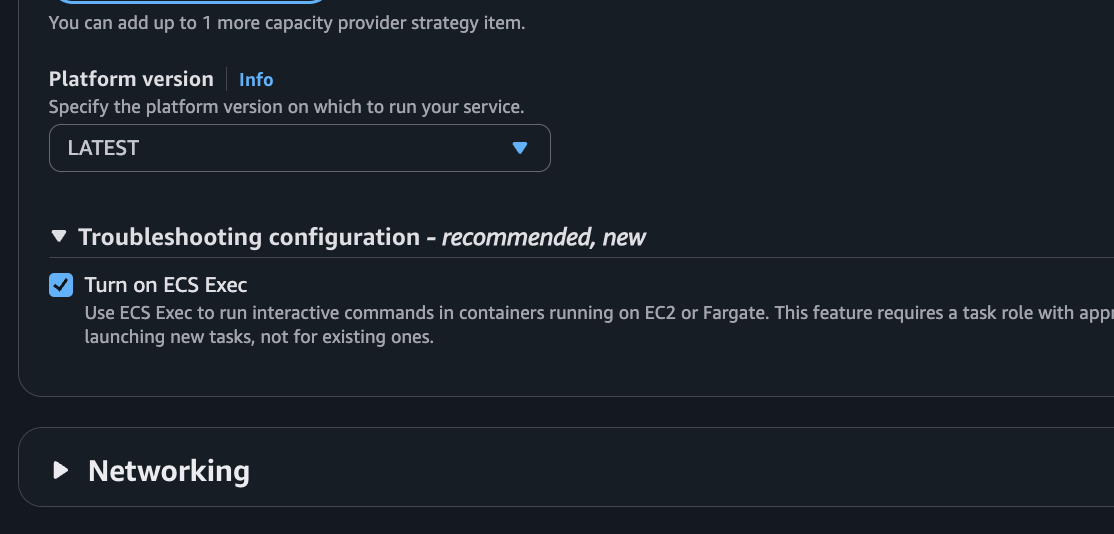
Step 2: Connect from the AWS Management Console
- Open the ECS Console.
- Navigate to your cluster → Tasks → Select a task.
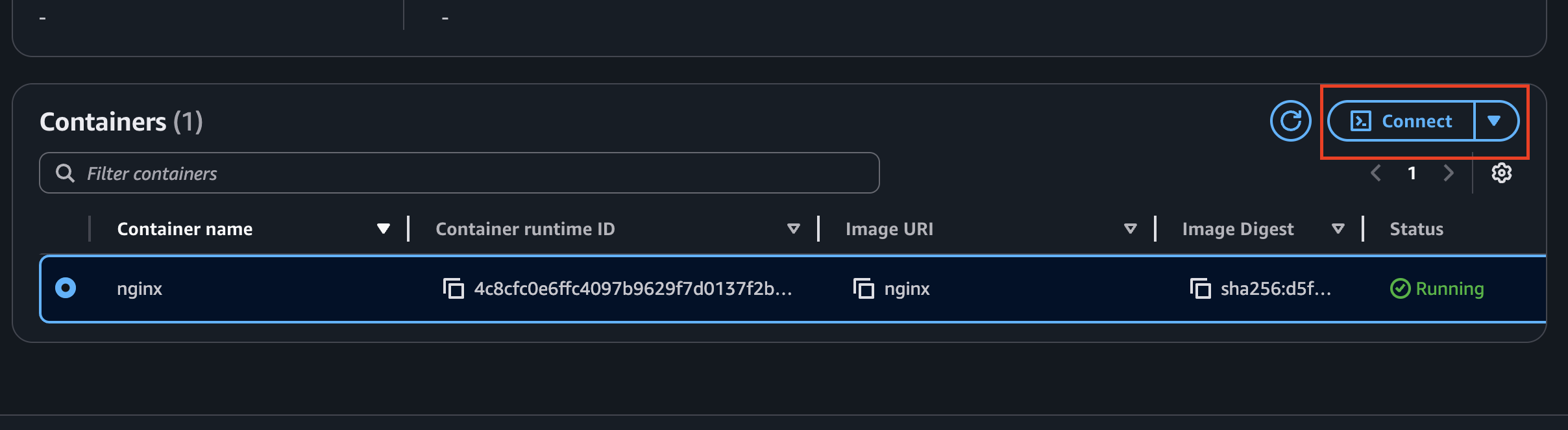
- Choose the container you want.
- Click “Connect” → Execute Command.
- A CloudShell session opens with direct access to your container.
As shown in the screenshot below:
Step 3: Run Commands Inside the Container
For example:
# Check running processes
ps aux
# View application logs
cat /var/log/app.log
# Debug network connections
netstat -tulpn
Step 4: Enable Logging (Optional but Recommended)
Capture all session activity to CloudWatch or S3:
aws ecs create-cluster \
--cluster-name exec-demo \
--configuration executeCommandConfiguration="{ \
kmsKeyId=your-kms-key-id, \
logging=OVERRIDE, \
logConfiguration={ \
cloudWatchLogGroupName=ecs-exec-logs, \
cloudWatchEncryptionEnabled=true, \
s3BucketName=my-exec-logs, \
s3EncryptionEnabled=true \
} \
}"
This ensures all commands and outputs are securely stored.
⚠️ Considerations & Limitations
- One ECS Exec session per PID namespace.
- Idle timeout of 20 minutes (non-configurable).
- Not supported on Nano Server containers.
- Requires updated AWS CLI (
>= v1.22.3or>= v2.3.6). - ECS Exec must be enabled before starting the task (not retroactive).
Conclusion
ECS Exec in the AWS Management Console is a game-changer for container troubleshooting, allowing you to securely connect to running containers without relying on SSH, managing inbound ports, or juggling CLI tools. With built-in support for logging, encryption, and fine-grained IAM policies, the feature is enterprise-ready, providing full auditability through CloudTrail, CloudWatch, or Amazon S3. Whether you’re a developer debugging locally or an operator handling critical production incidents, ECS Exec makes working with ECS containers faster, easier, and far more secure.